The LitmusChaos recommended in this issue is a cloud-native chaos engineering framework with cross-cloud support.
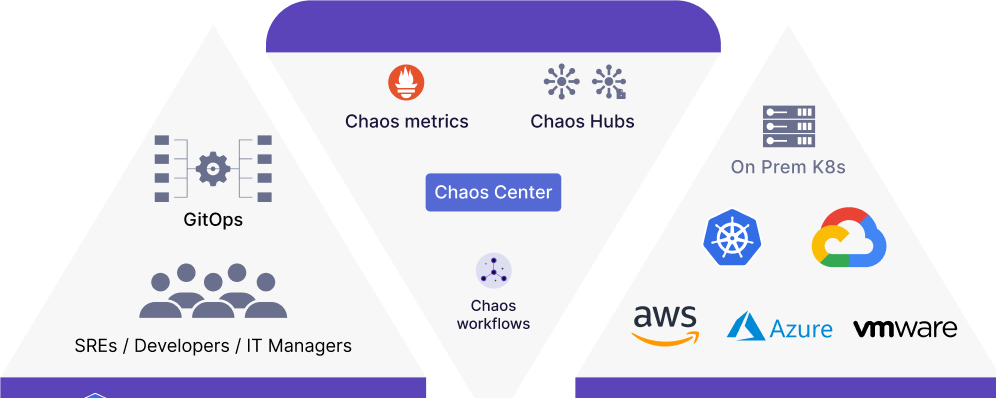
This is a CNCF sandbox project that has been adopted by several organizations. Its mission is to help Kubernetes SRE and developers find weaknesses in non-Kubernetes and platforms and applications running on Kubernetes by providing a complete chaos engineering framework and associated chaos experiments.
Litmus can initially be used to run chaos experiments in staging environments, and eventually in production environments to find errors and vulnerabilities, fix them, and improve the resilience of the system. Litmus takes a Kubernetes-native approach to define chaotic intent declaratively through custom resources.
Use case
- For developers: Run Chaos experiments during application development as an extension of unit testing or integration testing.
- For CI/CD pipeline builders: When the application encounters a fault path in the pipeline, run Chaos as a pipeline phase to find errors.
- For SRE: Plan and arrange chaotic experiments of applications and/or surrounding infrastructure. This approach can identify weaknesses in deployed systems and improve resilience.
The importance of Litmus
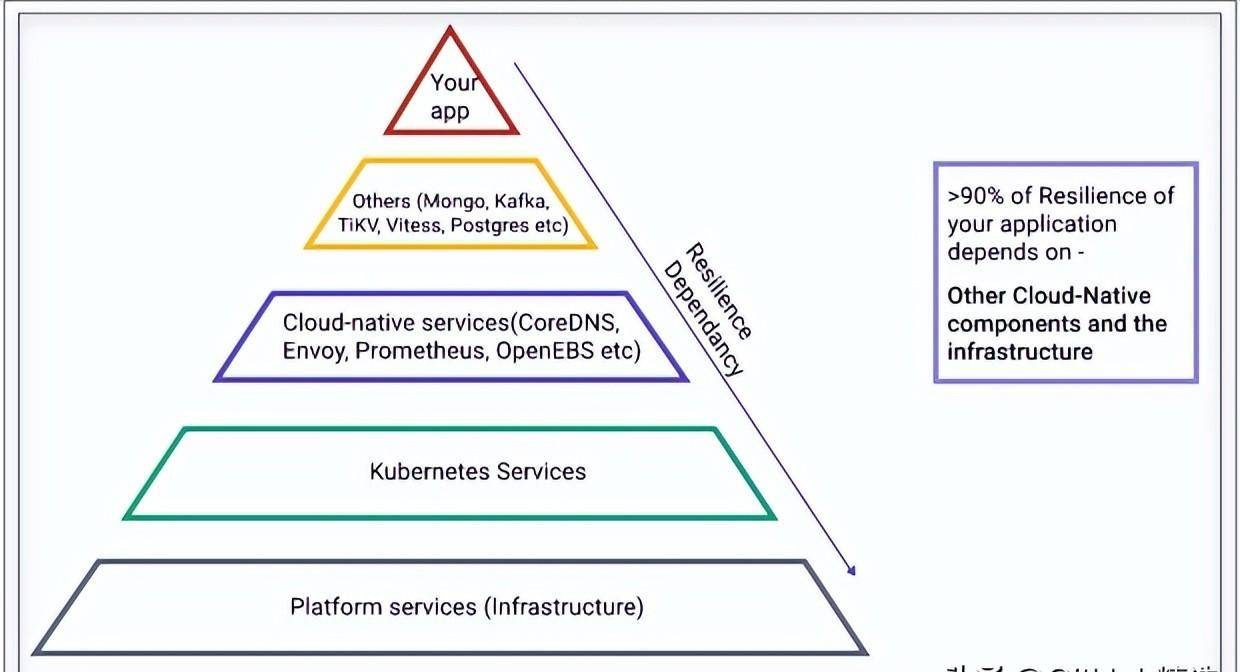
Kubernetes is running on a variety of infrastructures, from virtual machines to bare metal machines and combinations of them. The physical nature of the platform is a source of failure for applications running inside containers, as shown in the tip above. The next layer of dependency is Kubernetes itself.
Your application’s resiliency actually depends more on the underlying stack than on your application itself. Once your application is stable, the resiliency of your services running on Kubernetes may depend on other components and infrastructure more than 90% of the time.
Therefore, it is important to verify your application resilience whenever the underlying stack changes. Constant validation of is key. The robustness test before the upgrade is not good enough, mainly because it is impossible to take into account various failures during the upgrade test. This introduces the concept of chaos engineering. The process of “ constantly verifying that your service is fail-proof” is called Chaos engineering.
Litmus feature
- Add Chaotic workflow creation, Chaos experiments become the building blocks of chaotic workflow, allowing users to create larger chaotic scenes using sequential or parallel experiment execution.
- added ChaosCenter where you can take advantage of all these features and more
Workflow creation
- Custom workflows from the template, from scratch (using ChaosHubs), from pre-created YAML
- Chaotic experimental sequence control (parallel and sequential step creation)
- Creates the Singular or Cron workflow as a plan
- Prioritize chaos experiments according to your use case
User and team
- Creating users with role-based access control
- Create a team of multiple users
- Validate user
Monitoring and observability
- Connect to data sources (from any agent) and monitor workflows
- Visualizing workflow running statistics and summary plans
- Compare two or more workflows
- Upload shared/downloadable dashboards available in the community
- Edit queries, adjust dashboards to create custom dashboards from scratch
- Monitor the impact of chaos in real time using interlaced events and metrics from Prometheus data sources
Workflow management
- Use GitOps to roll out automatic changes
- Allows adding images from custom image servers (public and private)
- Measure and analyze elasticity scores for each workflow
Litmus itself is composed of microservices. We made sure to integrate additional microservices seamlessly with existing microservices by adding the above features for 2.0. Litmus 2.0 is fully backward compatible. No features are deprecated.
Resources
ChaosCenter is a single source of fact that controls all the different chaotic activities occurring around Litmus. From ChaosCenter, you have the freedom to manage every part of Litmus and shape your workflow exactly the way you want.
The ChaosAgent in Litmus is nothing more than the target cluster of Chaos injected through Litmus. There should always be at least one or more Chaosagents connected to ChaosCenter. Each individual ChaosAgent can be selected as the target agent for Chaos Injection.
In Litmus, ChaosAgent can be divided into two types
- Self-agency
- External agent
Self Agent will be registered as the default agent in ChaosCenter as part of the Litmus installation. The installer selects the same cluster on which Litmus is installed as Self Agent. Now you can introduce chaos to the Self Agent from ChaosCenter and observe the results.
Because ChaosCenter is cross-cloud, you can connect multiple external Kubernetes agents to the same station with the command-line utility litmusctl. Once connected, you can manage, monitor, observe, and induce chaos from ChaosCenter to the corresponding ChaosAgent.
ChaosCenter Cluster range installation
< Use helm
Step 1: add litmus helmhelm install chaos litmuschaos/litmus –namespace=litmushelm repo add litmuschaos
https://litmuschaos.github.io/litmus-helm/helm repo list
Step 2: Create Litmus
- ChaosCenter can be placed in any namespace, but in this case we choose litmus as the namespace.
kubectl create ns litmusStep 3: Install Litmus
helm install chaos litmuschaos/litmus --namespace=litmusExpected output
NAME: chaos
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Jun 15 19:20:09 2021
NAMESPACE: litmus
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Thank you for installing litmus
Your release is named chaos and its installed to namespace: litmus.
Visit https://docs.litmuschaos.io to find more info.Note: Litmus uses Kubernetes CRD to define chaos intent. Helm3 handles CRD better than Helm2. Before you start running your Chaos experiment, verify that Litmus is installed correctly.
Use kubectl
The application manifest file will install all the required service account configurations and ChaosCenter.
kubectl apply -f https:/ / litmuschaos. Making. IO/litmus < / span > < span class = "HLJS - regexp" > / 2.8.0 litmus < / span > - < span Class = "HLJS - number" > 2.8 < / span > < span class = "HLJS - number" > 0 < / span >. The yaml < / code > < / pre >Verify installation
Verify that front-end, server, and database Pods are present by checking the pods in the namespace where Litmus is installed:
kubectl get pods -n litmusExpected output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
litmusportal-server-6fd57cc89-6w5pn 1/1 Running 0 57s
litmusportal-auth-server-7b596fff9-5s6g5 1/1 Running 0 57s
mongo-0 1/1 Running 0 57s
litmusportal-frontend-55974fcf59-cxxrf 1/1 Running 0 58sCheck the services running in the namespace where Litmus is installed:
kubectl get svc -n litmusExpected output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
litmusportal-frontend-service NodePort 10.43.79.17 <none> 9091:31846/TCP 102s
litmusportal-server-service NodePort 10.43.30.54 <none> 9002:31245/TCP,8000:32714/TCP 101s
litmusportal-auth-server-service NodePort 10.43.81.108 <none> 9003:32618/TCP,3030:31899/TCP 101s
mongo-service ClusterIP 10.43.227.10 <none> 27017/TCP 101s
mongo-headless-service ClusterIP None <none> 27017/TCP 101s访问
To set up and log into ChaosCenter, expand the available service you just created and copy PORT that
litmusportal-frontend-service
kubectl get svc -n litmus
HTTP: < span class = "HLJS - the comment" > / / 172.17.0.3:30385 / < / span > < / code > < / pre >172.17.0.3 Where is my NodeIP? 30385 is the front-end service port. If you use LoadBalancer, the only change is to provide one. LoadBalancerIP> :< PORT> Learn more about accessing ChaosCenter using LoadBalancer
You should be able to see the login page for Litmus ChaosCenter. Account password:
Username: admin
Password: litmus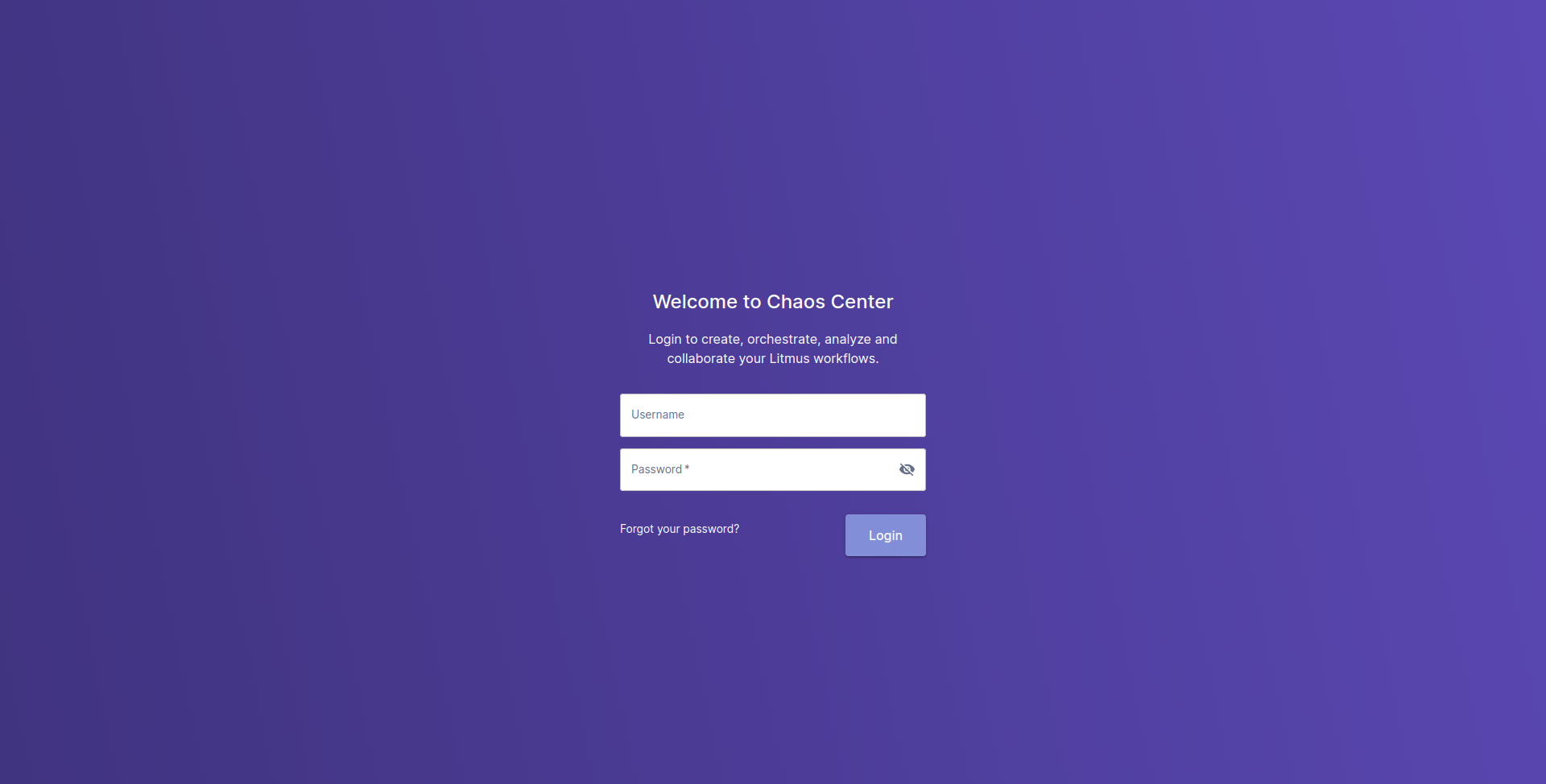
By default, you are assigned a default project with owner permissions.
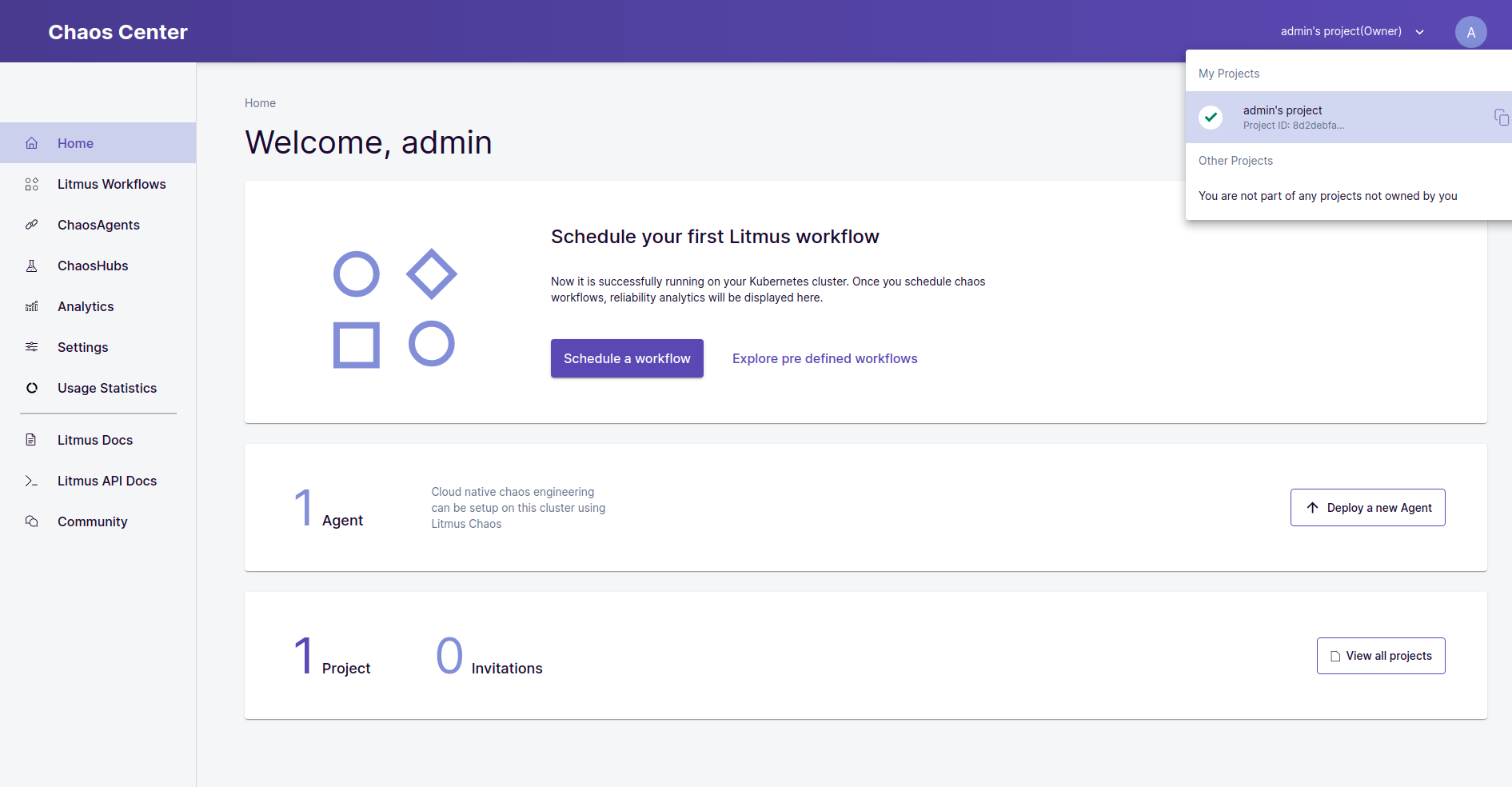
Run your first Chaos workflow in 5 minutes
- Click on the Schedule work process from the ChaosCenter home page or the Litmus Workflow TAB in the upper right corner.
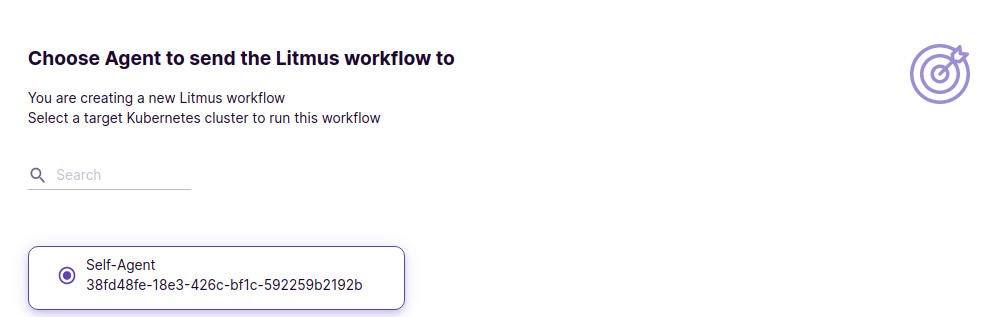
Select Self Agent ChaosAgent as the target of chaos injection. This is where we will choose which ChaosAgent to use as the target agent.
Expand the first radio button (Create a new workflow from a predefined workflow template) and select podtato-head from the list of predefined workflows.
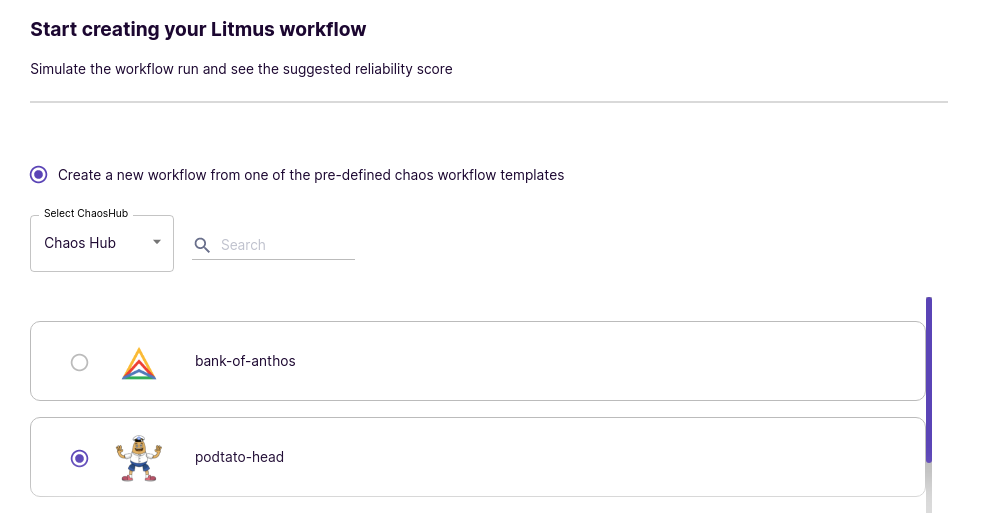
View Workflow details in Workflow Settings, where you can modify the name and description of the workflow as needed.
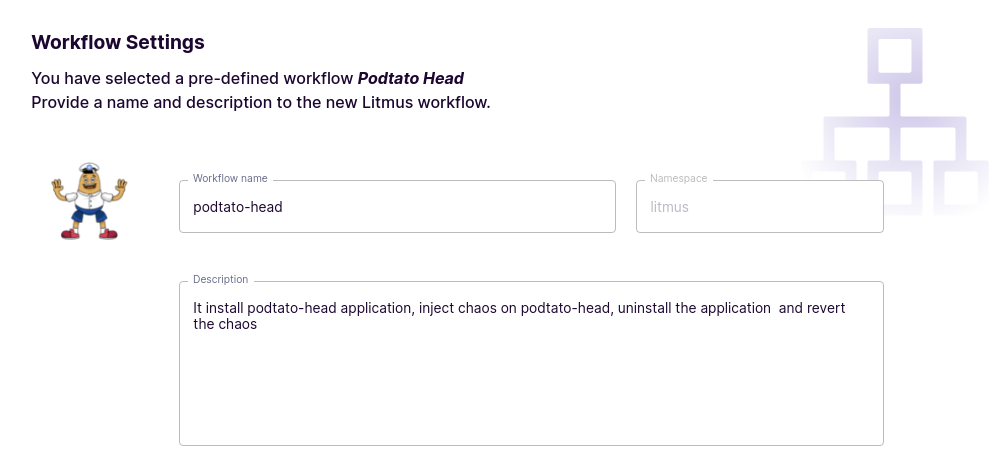
View a visualization of the Litmus workflow you will be performing. This step also allows you to edit or modify YAML/ tunable parameters if needed. We’ll stick to the default configuration for now.
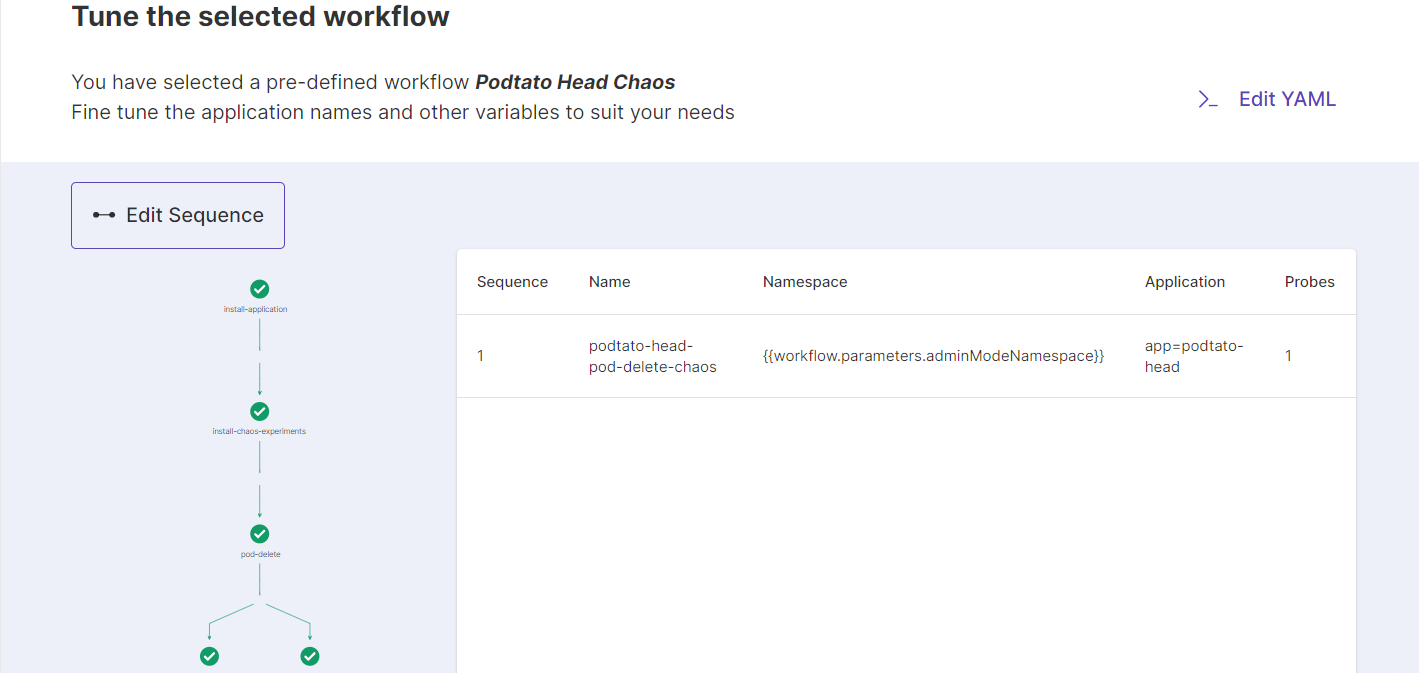
Use the slider to assign weights to chaos experiments that are part of the workflow. This is usually used when there are multiple experiments as part of the workflow. These weights affect the elasticity score calculation of the chaos workflow.
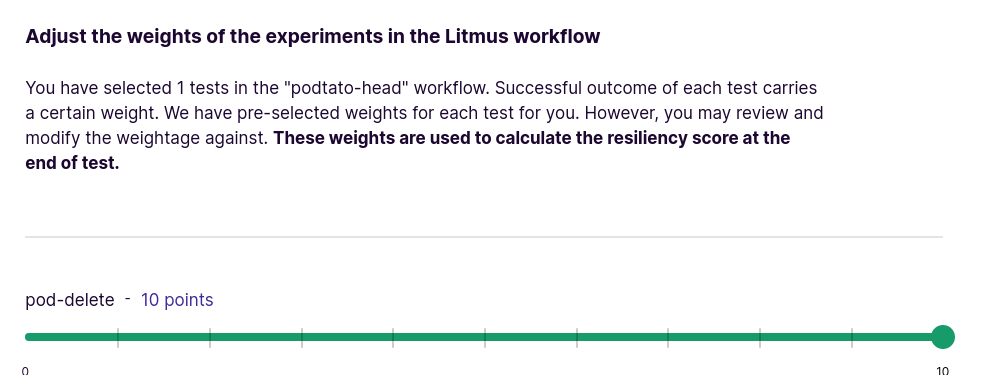
Schedule the Litmus workflow to execute
immediately and once by selecting the Schedule Now option
Validate and click to complete to start Chaos injection
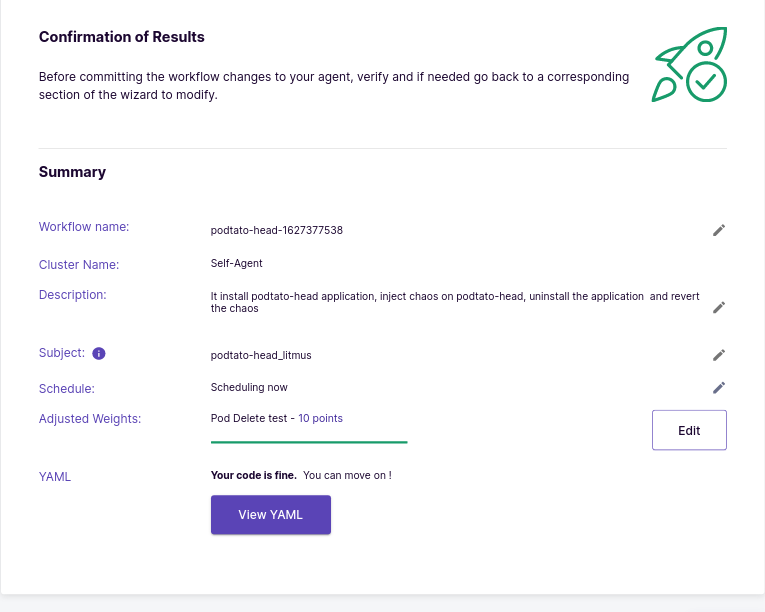
At this point, you have successfully arranged your first Chaos workflow using Litmus.

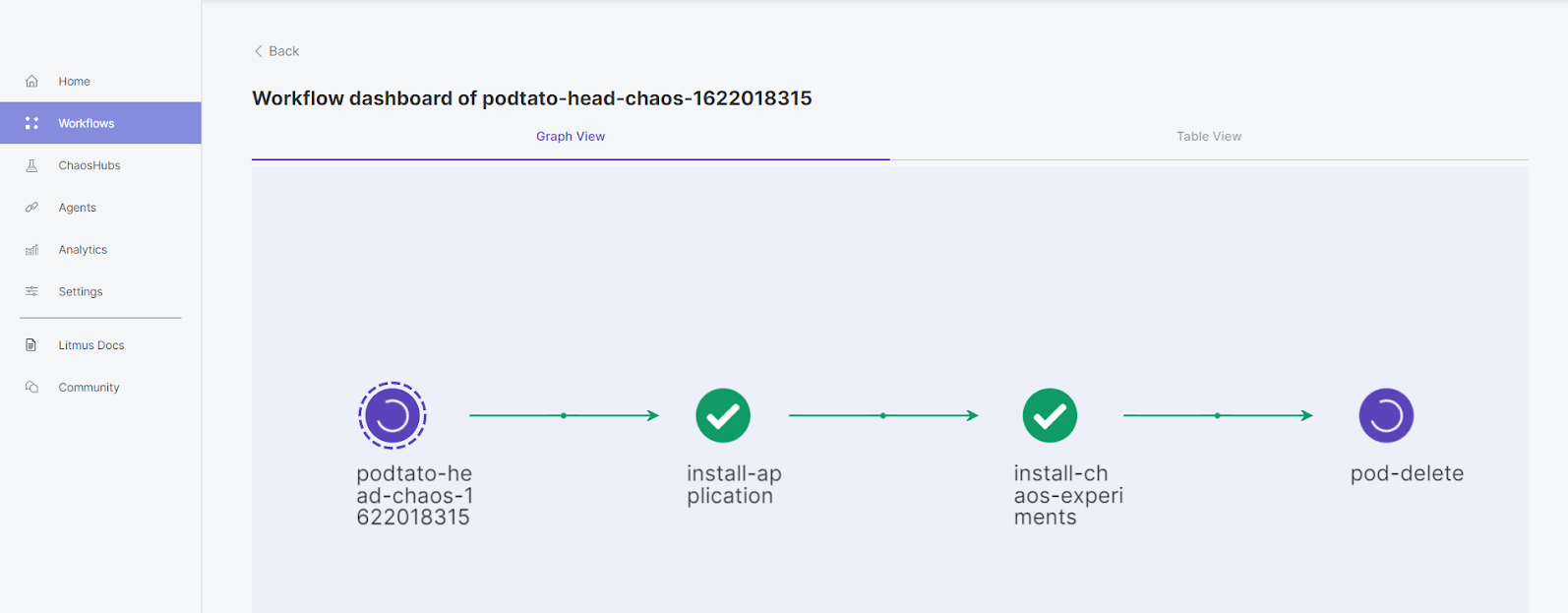
—END—
Open source protocol: Apache-2.0 license