This issue recommends a Go language RPC service governance framework – RPCX</ em>

RPCX is currently one of the most popular microservice frameworks in the Go ecosystem, used by many large companies and startups. The server does not require additional configuration, and RPCX also supports HTTP calls, allowing other programming languages to call RPCX services. It is currently one of the best performing RPC frameworks</ p>
Functional Features
- Easy to use: easy to get started, easy to develop, easy to integrate, easy to publish, easy to monitor
- High performance: The performance is much higher than frameworks such as Dubbo, Motan, Thrift, and is twice the performance of gRPC
- Cross platform, cross language: can be easily deployed on platforms such as Windows/Linux/MacOS, supporting calls from various programming languages
- Service discovery: In addition to direct connection, it also supports registration centers such as Zookeeper, Etcd, Consul, mDNS, etc
- Service governance: Supports failure modes such as failover, Fail fast, Fail try, Backup, etc., and supports routing algorithms such as random, polling, weight, network quality, consistent hashing, geographic location, etc
Quick Start
Install
Firstly, you need to install rpcx:
go get -u -v github.com/smallnest/rpcx/...</ code>This step will only install the basic features of rpcx. If you want to use etcd as a registry, you need to add the etcd tag</ p>
go get -u -v -tags "etcd" github.com/smallnest/rpcx/...</ code>If you want to use Quic, you also need to add the Quic tag</ p>
go get -u -v -tags "quic etcd" github.com/smallnest/rpcx/...</ code>For convenience, I recommend that you install all tags, even if you don’t need them now:
go get -u -v -tags "reuseport quic kcp zookeeper etcd consul ping" github.com/smallnest/rpcx/...</ code>Tags correspond to:
- Quic: Supports Quic protocol
- KCP: Supports KCP protocol
- Zookeeper: Supports Zookeeper Registry
- etcd: Supports etcd registry
- Consul: Supports Consul Registry
- Ping: Supports network quality load balancing
- Reuseport: Supports reuseport
Implement Service
Implementing a Sevice is like writing a simple Go struct:
import "context"
type Args struct {
A int
B int
}
type Reply struct {
C int
}
type Arith int
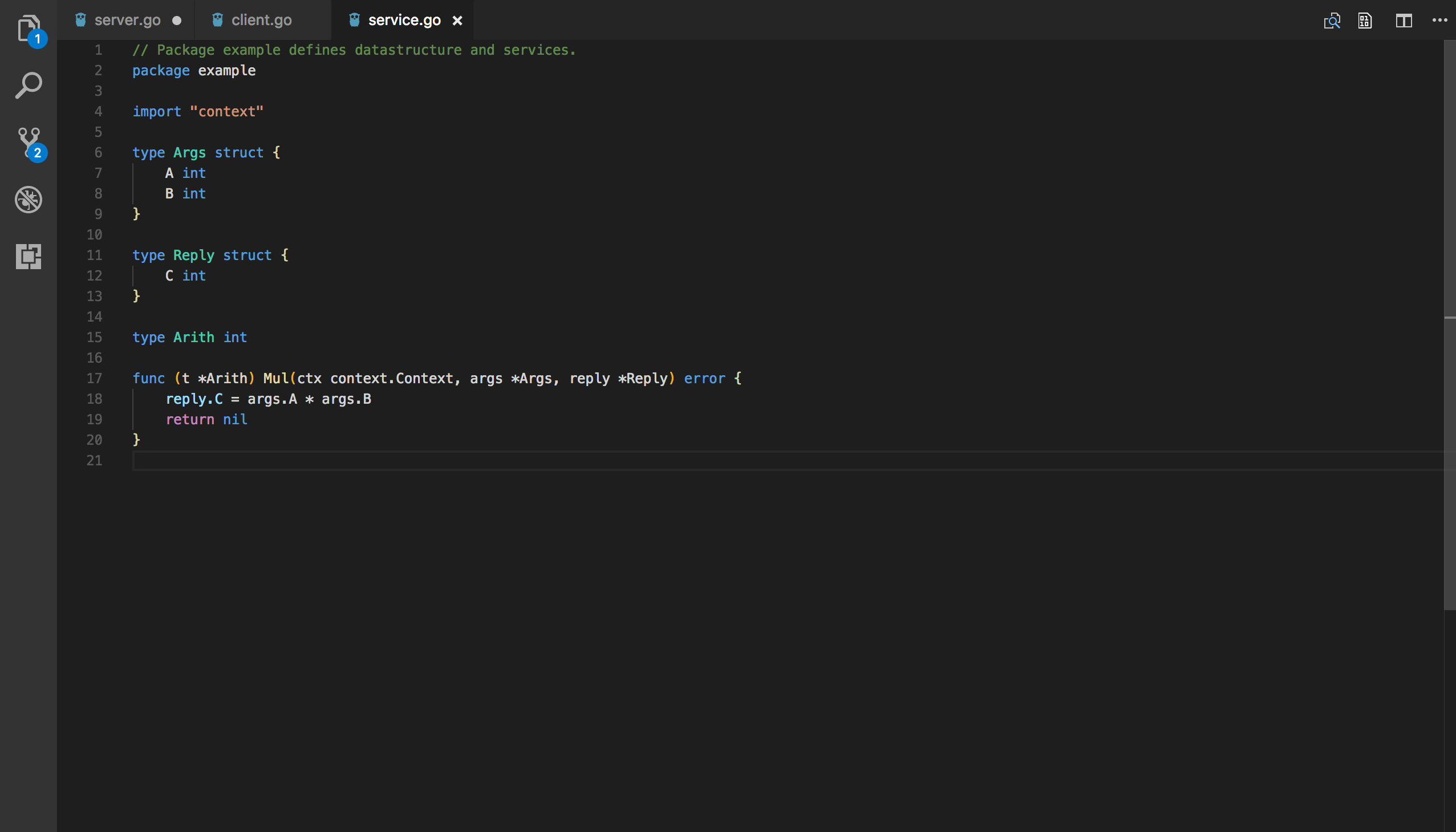
func (t *Arith) Mul(ctx context.Context, args *Args, reply *Reply) error {
reply.C = args.A * args.B
return nil
}Arith is a Go type and has a method called Mul. The first parameter of method Mul is context Context。 The second parameter of the Mul method is ARGs, which contains the requested data A and B. The third parameter of method Mul is reply, which is a pointer to the Reply structure. The return type of method Mul is error (which can be nil). Method Mul assigns the result of A * B to Reply C
Now you have defined a service called Arith and implemented the Mul method for it. In the next step, we will continue to introduce how to register this service with the server and how to call it with the client</ p>
Implement Server
Three lines of code can register a service:
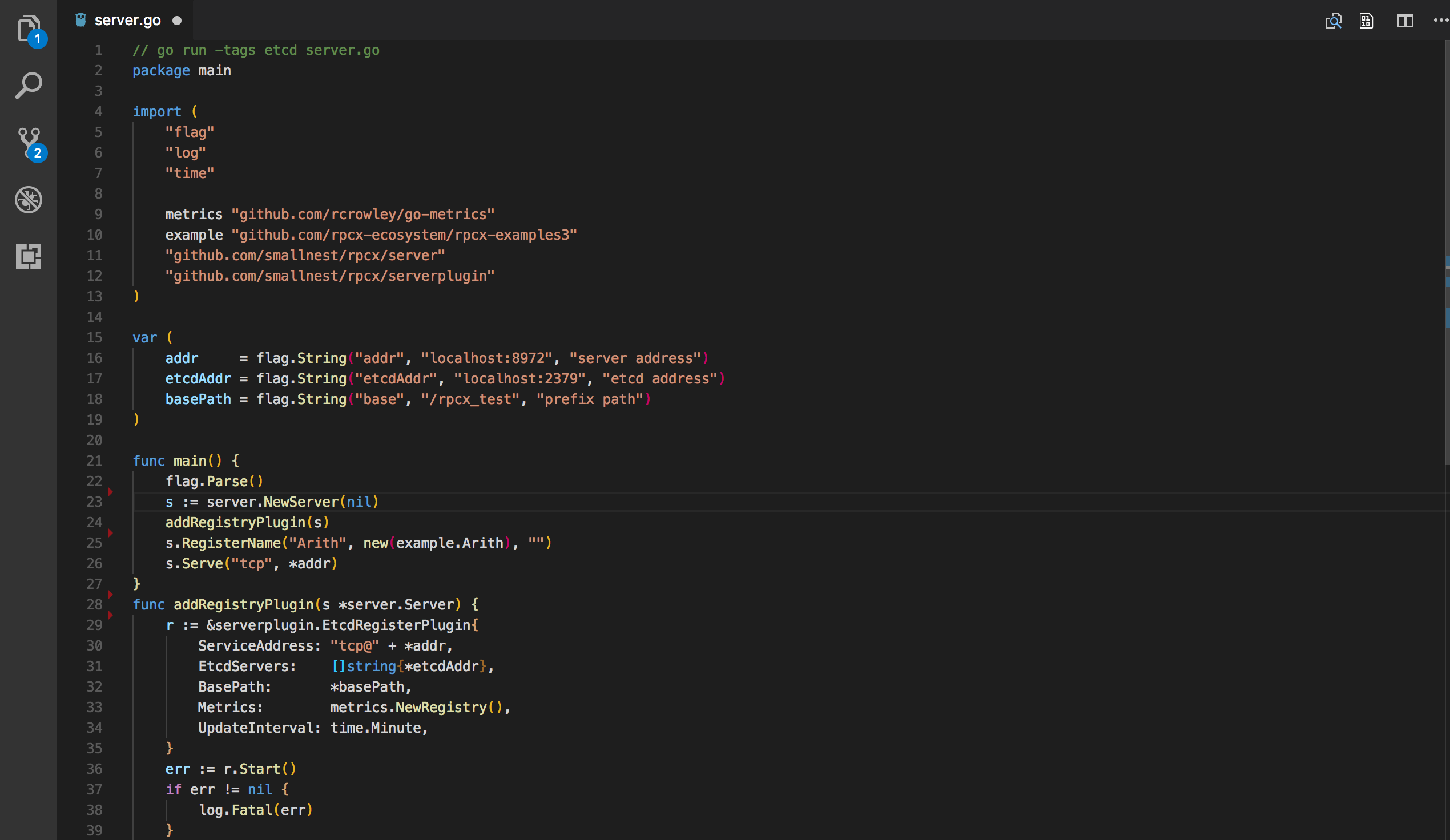
s := server. NewServer()
s.RegisterName("Arith", new(Arith), "")
s.Serve("tcp", ":8972")Here you name your service Arith</ p>
You can register for the service using the following code</ p>
s.Register(new(example.Arith), "")Here, the service type name is simply used as the service name</ p>
Implement Client
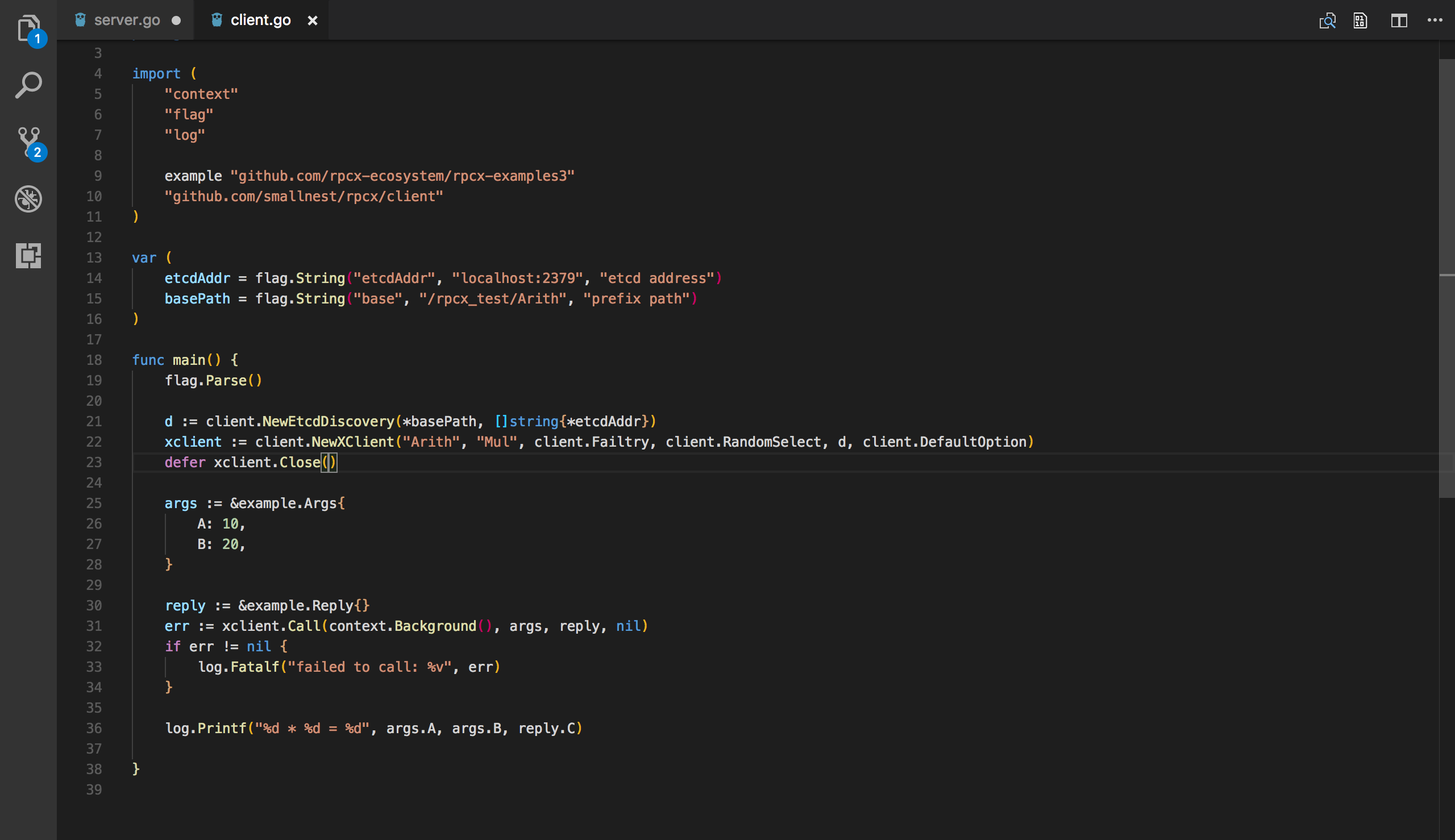
// #1
d := client.NewPeer2PeerDiscovery("tcp@"+*addr, "")
// #2
xclient := client.NewXClient("Arith", client.Failtry, client.RandomSelect, d, client.DefaultOption)
defer xclient. Close()
// #3
args := & example.Args{
A: 10,
B: 20,
}
// #4
reply := & example.Reply{}
// #5
err := xclient.Call(context.Background(), "Mul", args, reply)
if err != < span class="hljs-literal">nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to call: %v", err)
}
log.Printf("%d * %d = %d", args.A, args.B, reply.C)# 1 defines how to implement service discovery. Here we use the simplest Peer2PeerDiscovery. The client directly connects to the server to obtain the service address</ p>
# 2 created XClient and passed in Failed Mode, Select Mode, and default options. Failed Mode tells the client how to handle call failures: retry, fast return, or try another server. SelectMode tells the client how to select a server when multiple servers provide the same service</ p>
# 3 defines the request: here we want to get a result of 10 * 20. Of course, we can calculate the result ourselves to be 200, but we still want to confirm if this is consistent with the server’s return result</ p>
# 4 defines a response object with a default value of 0. In fact, rpcx uses it to know the type of the returned result and deserializes the result to this object</ p>
# 5 called a remote service and synchronized the results</ p>
Asynchronous call to Service
The following code can asynchronously call services:
d := client.NewPeer2PeerDiscovery("tcp@"+*addr2, "")
xclient := client.NewXClient("Arith", client.Failtry, client.RandomSelect, d, client.DefaultOption)
defer xclient. Close()
args := & example.Args{
A: 10,
B: 20,
}
reply := & example.Reply{}
call, err := xclient.Go(context.Background(), "Mul", args, reply, nil)
if err != < span class="hljs-literal">nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to call: %v", err)
}
replyCall := <- call.Done
if replyCall. Error != < span class="hljs-literal">nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to call: %v", replyCall.Error)
} else {
log.Printf("%d * %d = %d", args.A, args.B, reply.C)
}You must use xcerver Go to replace xcerver Call and return the result to a channel. You can listen for the call results from chnenel</ p>
Performance testing
Test Environment
-
- CPU : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2630 v3 @ 2.40GHz, 32 cores
- Memory: 32GB
- Go version: 1.9.0
Operating System: CentOS 7/3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64
Adopt
- protobuf
- The client and server are on the same server
- 581 byte payload
- 500/2000/5000 concurrent clients
- Simulation processing time: 0ms, 10ms, and 30ms
Test results
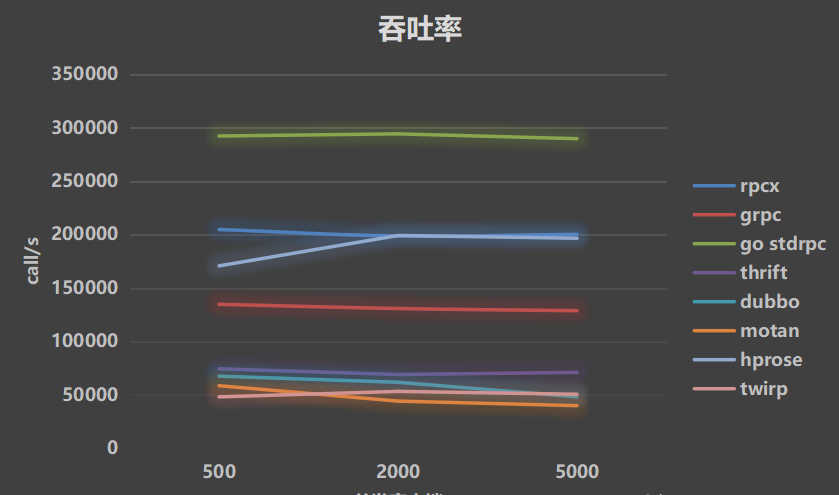
Simulate 0ms processing time:
- Throughput
- Average latency
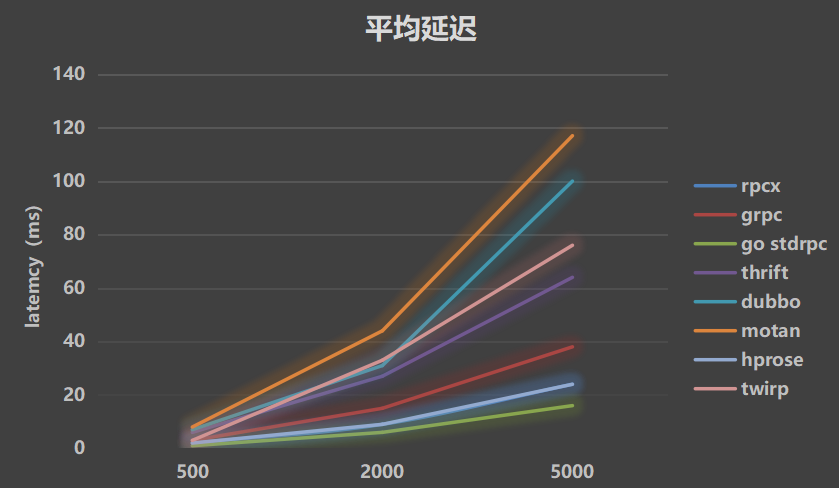
- P99 latency
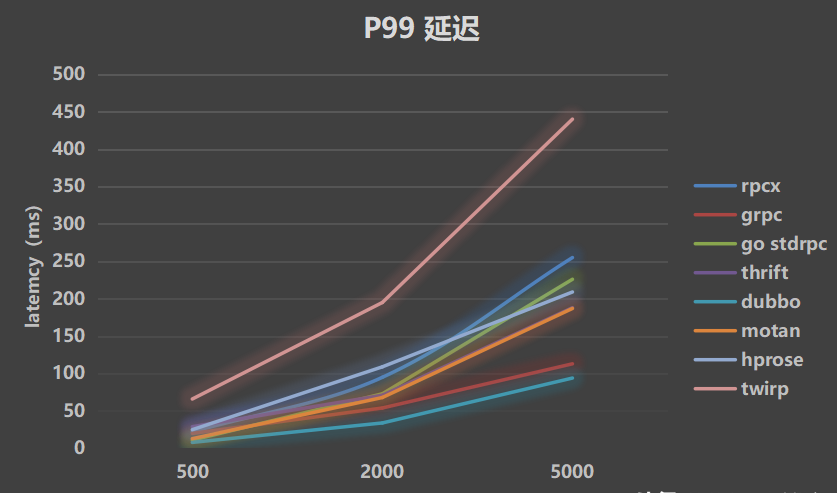
Simulate 10ms processing time:
- Throughput
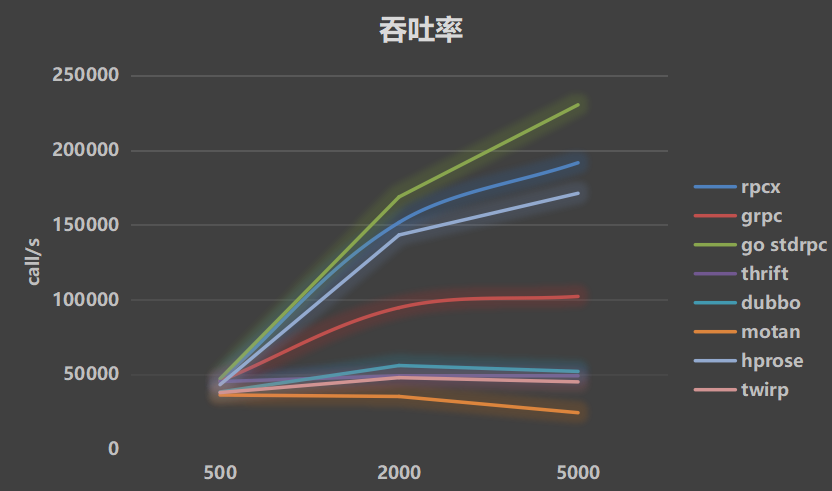
- Average latency
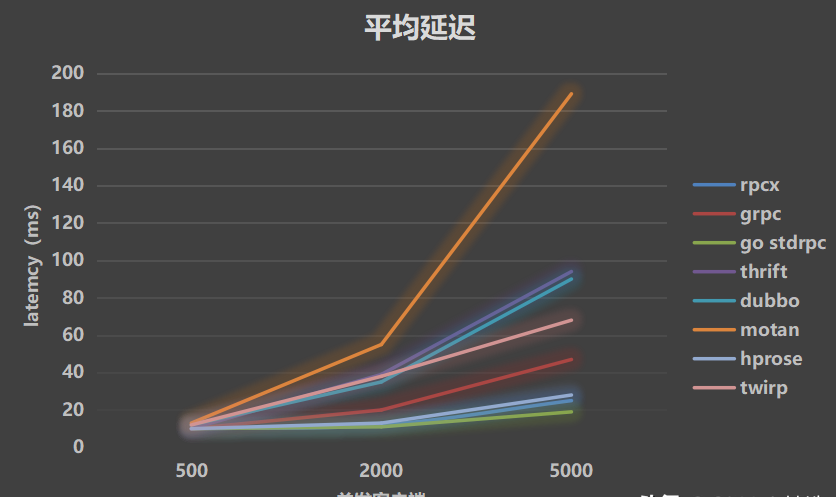
- P99 latency
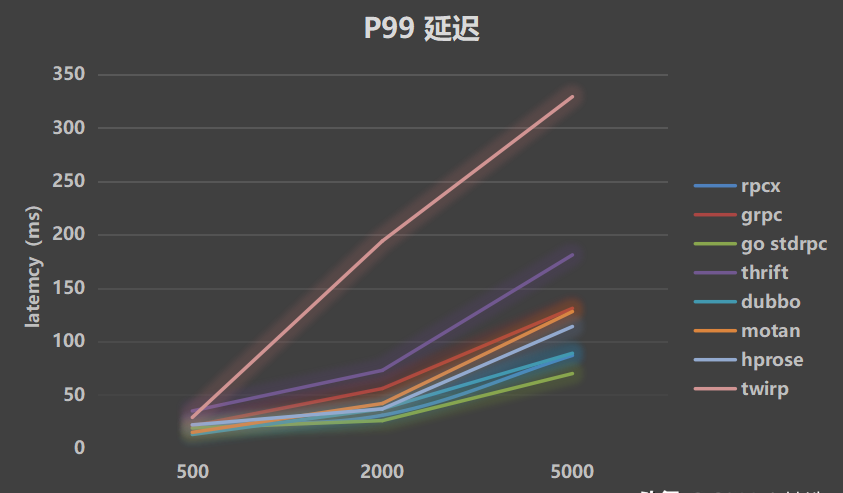
Simulate 30ms processing time:
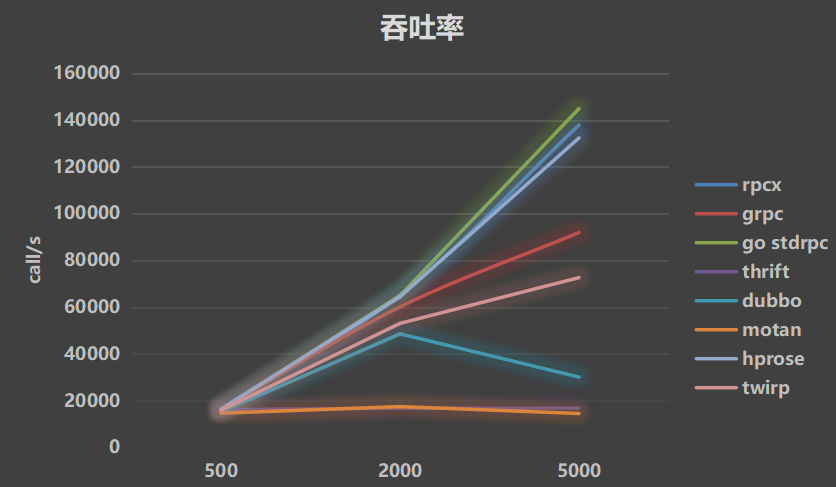
- Throughput
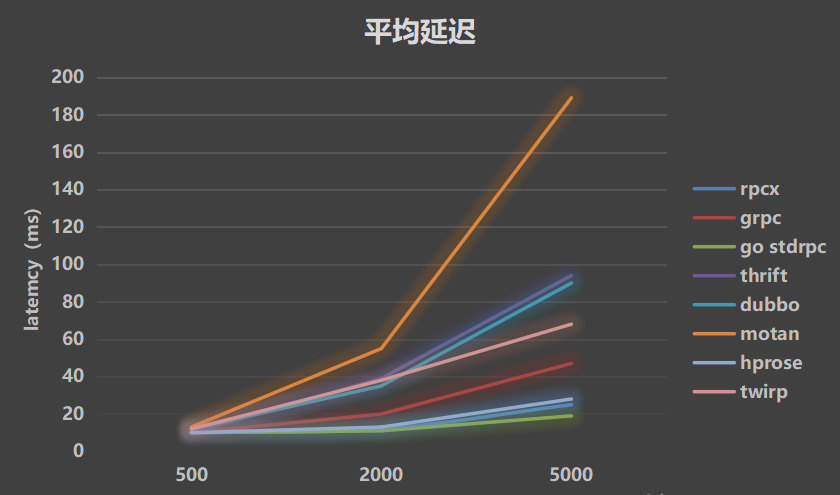
- Average latency
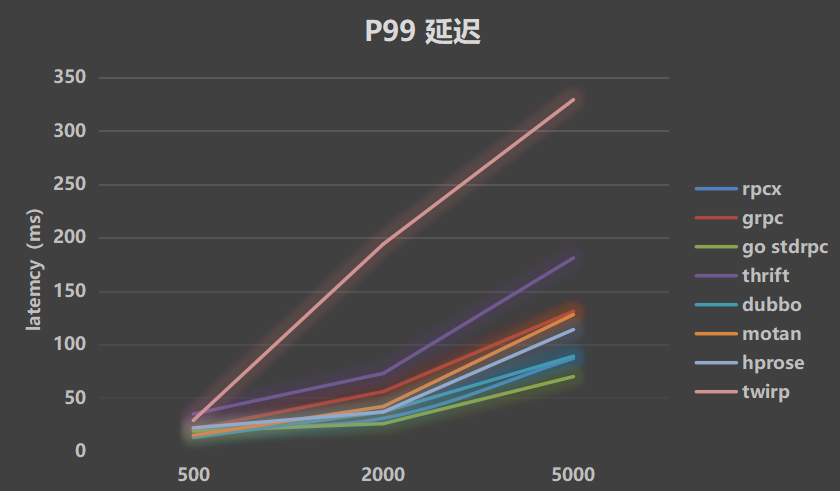
- P99 latency
—END—
Open source license: Apache 2.0