Sa-Token is a lightweight Java permission authentication framework, mainly to solve: login authentication, permission authentication, Session session, single sign-on, OAuth2.0, microservice network authentication and a series of permissions related issues.
Overview of Sa-Token functions:
Login authentication – single-end login, multi-end login, mutually exclusive login, no login within seven days
Permission authentication: Permission authentication, role authentication, and session level-2 authentication
Session Session: All-end shared Session, single-end exclusive Session, and customized session
Kick a user offline: Kick a user offline based on the account id and Token value
Account blocking – designated days of blocking, permanent blocking, set unblocking time
Persistence layer extension – can integrate Redis, Memcached and other professional cache middleware, restart data without loss
Distributed session – Provides two distributed session solutions for jwt integration and shared data centers
Microservice authentication – Route blocking authentication for common gateways such as Gateway, ShenYu, and Zuul
Single sign-on – Three single sign-on modes are built in: cross-domain, shared Redis or not
OAuth2.0 authentication — Based on RFC-6749 standard, OAuth2.0 standard process of authorization authentication, support openid mode
Level 2 authentication: Re-authentication on the basis of login to ensure security
Basic Authentication – A line of code accesses Http Basic authentication
Standalone Redis – Separate the permission cache from the business cache
Temporary Token authentication – Solves the problem of short-term Token authorization
Simulate other accounts – manipulate any user status data in real time
Temporary Identity switching – Temporarily switching the session identity to another account
Separation of front and back – APP, small program and other terminals that do not support cookies
The same terminal is mutually exclusive login – like QQ mobile phone computer online at the same time, but the two mobile phones are mutually exclusive login
Multi-account authentication system – for example, the user table and admin table of a mall project are authenticated separately
Fancy token generation – built-in six Token styles, also can: custom Token generation strategy, custom Token prefix
Annotated authentication – elegantly separates authentication from business code
Route interception authentication – Based on route interception authentication, the restful mode can be adapted
Automatic renewal – Provides two Token expiration policies, which can be flexibly used together and can be automatically renewed
Session governance – Provides a convenient and flexible session query interface
Remember Me mode – Adapt [Remember me] mode, restart the browser without verification
Password encryption – Provides password encryption module, can fast MD5, SHA1, SHA256, AES, RSA encryption
Global listener – performs some AOP operations when a user logs in, logs out, gets kicked off, and so on
Out of the box – Provides SpringMVC, WebFlux and other common web framework starter integration package, true out of the box
Sa-Token function structure: 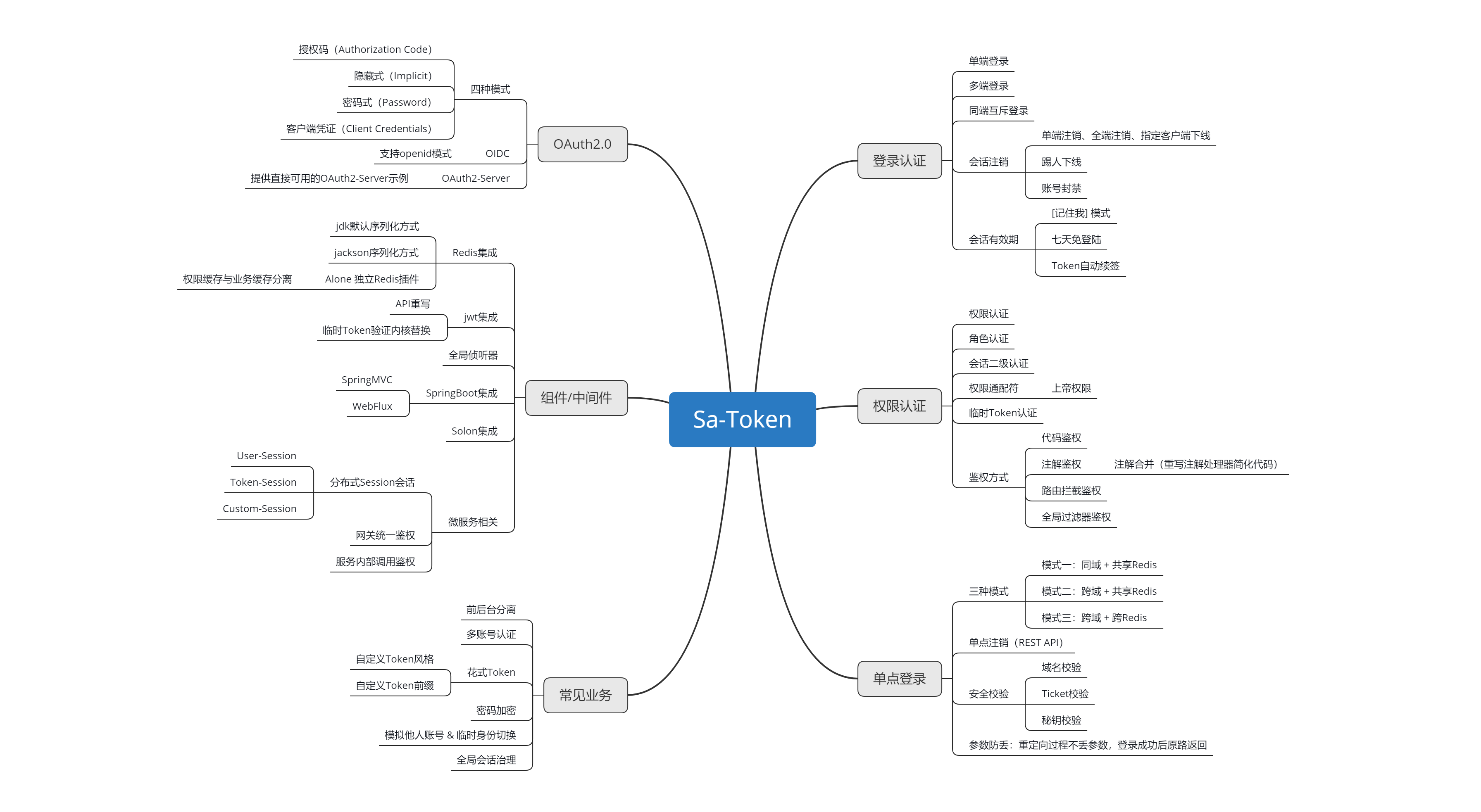
Introducing Dependencies (1 of 4):
- SpringMVC Environment
Maven dependency
<dependency><groupId>cn.dev33</groupId><artifactId>sa-token-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>1.27.0</version></dependency>Gradle dependency
implementation 'cn.dev33:sa-token-spring-boot-starter:1.27.0'- WebFlux Environment(Reactor)
Mavendependency
<dependency> <groupId>cn.dev33</groupId> <artifactId>sa-token-reactor-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.27.0</version></dependency>Gradledependency
implementation 'cn.dev33:sa-token-reactor-spring-boot-starter:1.27.0'- ServletContainer environment
Mavendependency
<dependency> <groupId>cn.dev33</groupId> <artifactId>sa-token-servlet</artifactId> <version>1.27.0</version></dependency>Gradledependency
implementation 'cn.dev33:sa-token-servlet:1.27.0'- else
Mavendependency
<dependency> <groupId>cn.dev33</groupId> <artifactId>sa-token-core</artifactId> <version>1.27.0</version></dependency>Gradledependency
implementation 'cn.dev33:sa-token-core:1.27.0'give a typical example:
The API design of Sa-Token is very simple, taking login authentication as an example, you only need to:
// The account of the current session is written during login :idStpUtil.login(10001);// Then call the following method where you want to verify the login:// 如果当前会话未登录,这句代码会抛出 `NotLoginException` 异常StpUtil.checkLogin();At this point, we have completed the login authentication with Sa-Token!
Permission authentication example (Only sessions with user:add permissions can enter the request)
@SaCheckPermission("user:add")@RequestMapping("/user/insert")public String insert(SysUser user) {// ... return "User increase";}Kick an account offline (throws a NotLoginException when the other party accesses the system again))
// Example Kick session 10001 offline StpUtil.kickout(10001);In Sa-Token, most functions can be done with a single line of code:
StpUtil.login(10001); // Mark the account for which the current session is logged in idStpUtil.getLoginId(); // 获取当前会话登录的账号idStpUtil.isLogin(); // 获取当前会话是否已经登录, 返回true或falseStpUtil.logout(); // 当前会话注销登录StpUtil.kickout(10001); // 将账号为10001的会话踢下线StpUtil.hasRole("super-admin"); // 查询当前账号是否含有指定角色标识, 返回true或falseStpUtil.hasPermission("user:add"); // 查询当前账号是否含有指定权限, 返回true或falseStpUtil.getSession(); // 获取当前账号id的SessionStpUtil.getSessionByLoginId(10001); // 获取账号id为10001的SessionStpUtil.getTokenValueByLoginId(10001); // 获取账号id为10001的token令牌值StpUtil.login(10001, "PC"); // 指定设备标识登录,常用于“同端互斥登录”StpUtil.kickout(10001, "PC"); // 指定账号指定设备标识踢下线 (不同端不受影响)StpUtil.openSafe(120); // 在当前会话开启二级认证,有效期为120秒 StpUtil.checkSafe(); // 校验当前会话是否处于二级认证有效期内,校验失败会抛出异常 StpUtil.switchTo(10044); // 将当前会话身份临时切换为其它账号谁在使用Sa-Token:


You can read more on your own。
If you need project recommendations and resources, please send private letters to the author